Understanding the Role of an Oncology Specialist
In today's world, where cancer remains one of the leading health challenges, the role of an oncology specialist has become increasingly significant. As experts in diagnosing and treating various forms of cancer, these professionals are at the forefront of innovative treatments and patient care strategies. This comprehensive article will delve deeply into what it means to be an oncology specialist, the different types of oncologists, the role they play in patient management, and the importance of their work in the broader context of healthcare and medical research.
What is an Oncology Specialist?
An oncology specialist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Oncologists are skilled in managing cancer care comprehensively, often working closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, including surgeons, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals. Their expertise spans a range of cancer types, treatment modalities, and supportive care strategies.
Types of Oncology Specialists
Oncology is a vast field with several sub-specialties, each focusing on different aspects of cancer care. Here are the primary types of oncology specialists:
- Medical Oncologists: These are the doctors who manage cancer treatment through chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. They are often the primary oncologist a patient sees after a cancer diagnosis.
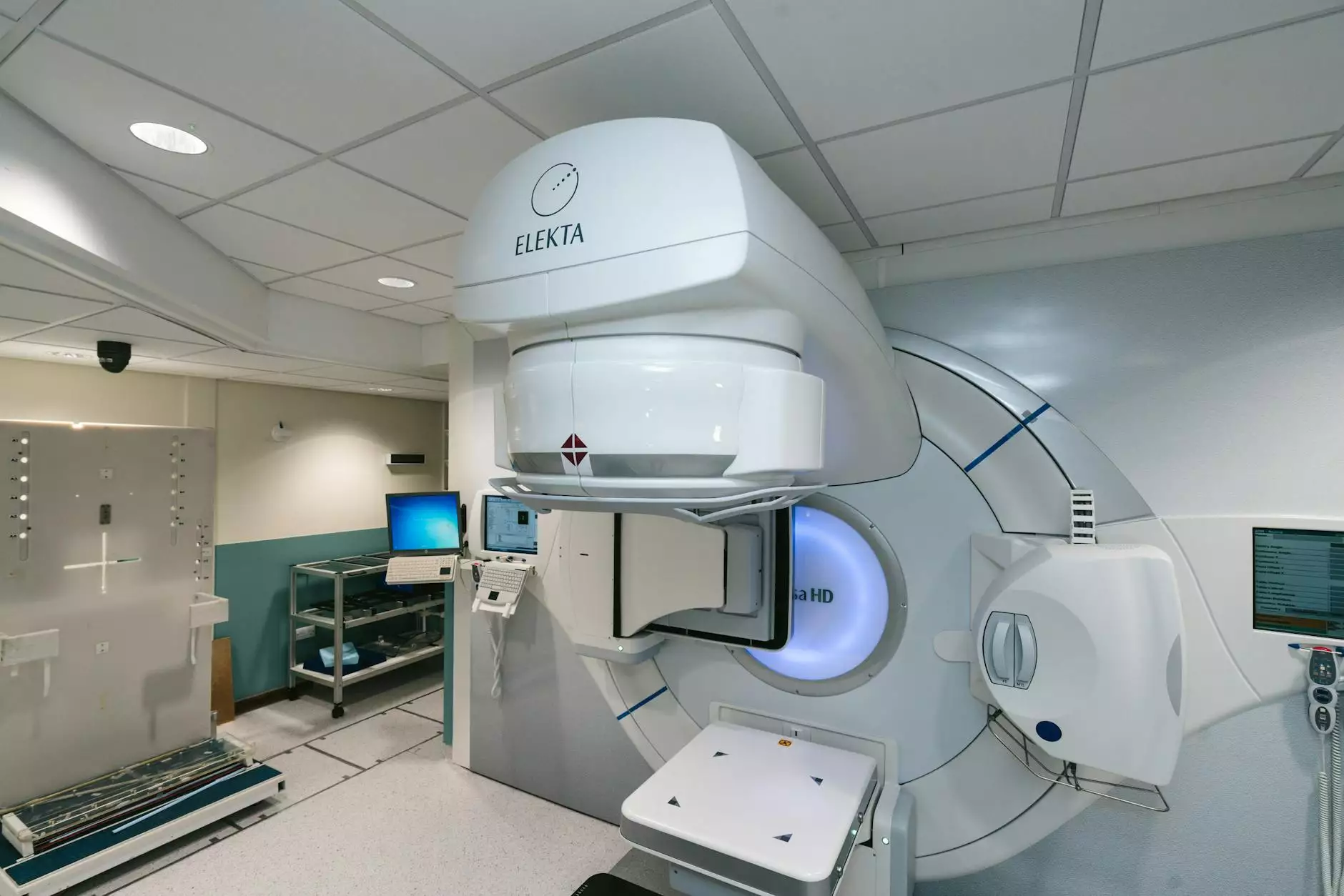
- Radiation Oncologists: Specialists who administer radiation therapy to treat cancer. They design treatment plans using advanced technology to target cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Surgical Oncologists: Physicians who perform surgeries to remove tumors and cancerous tissues. They also play a role in staging the cancer and determining the most effective treatment plan.
- Pediatric Oncologists: These specialists focus specifically on diagnosing and treating cancer in children. They tailor treatment approaches to the developing bodies of pediatric patients.
- Gynecologic Oncologists: Specialists who diagnose and treat cancers related to the female reproductive system, including ovarian, uterine, and cervical cancers.
- Urologic Oncologists: Focused on cancers of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, including prostate and bladder cancer.
The Importance of Oncology Specialists in Cancer Care
The treatment of cancer is complex and requires a tailored approach to each patient. An oncology specialist enhances the quality of care provided to cancer patients in several ways:
1. Personalized Treatment Plans
Each cancer case is unique, requiring a specialized approach. Oncology specialists use their expertise to create personalized treatment plans that consider the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
2. Advanced Knowledge of Cancer Biology
Oncology specialists possess in-depth knowledge of cancer biology, which allows them to understand the mechanisms of cancer growth and metastasis. This knowledge is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and can lead to more successful outcomes for patients.
3. Multidisciplinary Collaboration
Oncology is rarely a solo endeavor. An oncology specialist works within a multidisciplinary team that includes surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, nurses, and social workers. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care that addresses not just the cancer but the overall well-being of the patient.
4. Access to Clinical Trials
Oncology specialists often have access to the latest research and clinical trials, providing patients with opportunities to participate in cutting-edge studies that may offer new treatment options not yet available in general practice.
The Role of an Oncology Specialist in Patient Care
When a patient is diagnosed with cancer, the journey can be overwhelming. An oncology specialist plays a pivotal role in guiding them through this journey. Here’s how:
1. Diagnosis and Staging
Accurate diagnosis and staging of cancer are crucial for effective treatment. Oncology specialists use various diagnostic tools, including:
- Imaging tests (CT scans, MRIs, PET scans)
- Biopsies
- Blood tests
These tools help oncologists determine the cancer type, location, size, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
2. Treatment Options and Management
After an accurate diagnosis, the oncology specialist discusses various treatment options with the patient. These may include:
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from dividing.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Surgery: Removing cancerous tissue from the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Using drugs that target specific aspects of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Treatment that helps the immune system fight cancer.
The choice of treatment depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient's health, preferences, and lifestyle.
3. Ongoing Support and Management
Beyond initial treatment, oncology specialists provide ongoing support to manage side effects and monitor for any recurrence of cancer. This includes:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Symptom management
- Pain management
- Psychosocial support and counseling
The holistic care provided by an oncology specialist contributes to the patient's quality of life and emotional well-being during and after treatment.
Education and Training of an Oncology Specialist
Becoming an oncology specialist requires extensive education and training:
1. Medical Degree
Prospective oncology specialists begin by obtaining a bachelor's degree, followed by a medical degree (MD or DO) from a recognized medical school.
2. Residency Training
After completing medical school, candidates undergo residency training in internal medicine, general surgery, or pediatrics. This typically lasts three to five years, providing a broad base in general medicine.
3. Fellowship in Oncology
Following residency, doctors may pursue additional fellowship training in oncology, which lasts two to three years. During this period, they gain specialized knowledge and hands-on experience in cancer care.
4. Board Certification
Once training is complete, oncology specialists may seek board certification through recognized medical boards, validating their expertise in the field.
The Future of Oncology Specialists
The field of oncology is rapidly evolving, with advances in research and technology paving the way for new treatment modalities and improved patient outcomes. Here are key emerging trends:
- Precision Medicine: Utilizing genetic profiling of tumors to create personalized treatment plans.
- Telemedicine: Expanding access to oncology care through virtual consultations, particularly important in rural and underserved areas.
- Advancements in Immunotherapy: Continued research into immunotherapy offers hope for more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
- Cancer Prevention and Screening: Ongoing research into preventive measures aims to reduce cancer incidence and improve early detection rates.
As oncology specialists embrace these innovations, their role will become even more integral to improving cancer care and outcomes.
Conclusion
The expertise of an oncology specialist is invaluable in the fight against cancer. Through personalized care, collaborative treatment approaches, and ongoing support, they significantly impact the lives of patients facing this formidable disease. As research continues to evolve and new treatments emerge, oncology specialists will remain at the forefront of cancer care, helping to provide hope and healing to those affected by cancer.








